Exposure to fumes from metalworking fluids poses a potential risk to machine operators. The best way to avoid health problems is to install a risk and fluid management program and choose safe and healthy products.
Inhalation of mist from pure soluble metalworking fluids can lead to respiratory diseases such as COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) and EAA (extrinsic allergic alveolitis), also known as hypersensitivity pneumonitis.
Employers must ensure that adequate measures are taken to reduce operator exposure to mists.
how fog is formed
Metalworking fluids are complex mixtures of carefully selected chemicals designed to perform multiple functions in the metal fabrication process. Metalworking fluids can vary widely in composition and composition.
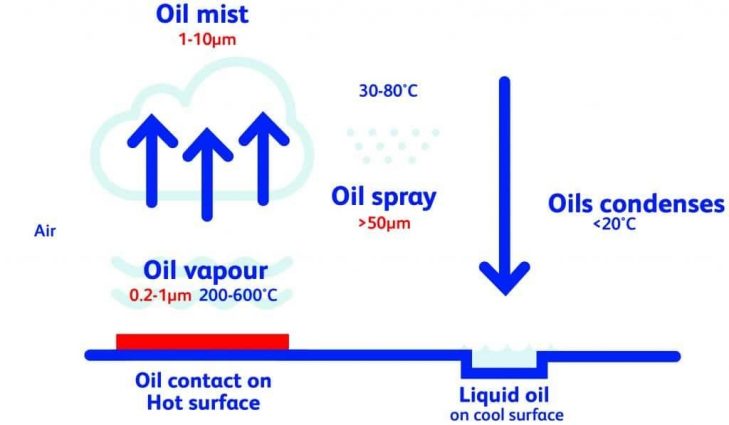
All fluids have some tendency to form aerosols or mists. This tendency depends on the type and condition of the fluid and the surrounding environment.
Atomization is the formation of liquid particles suspended in the air
Oil mist may form when oil is sprayed with high pressure or when oil comes in contact with hot surfaces and evaporates. It condenses when it comes in contact with relatively cold air temperatures. This occurs when fluids interact with moving parts during machining.
Hazards of metalworking fluid mist
Smoke inhalation is strongly linked to cancer and occupational asthma. There is also a risk of lung disease and breathing problems because chemicals and microbes can irritate the lungs. People who already have asthma may irritate this. Conditions can range from mild to extreme and subsequently affect quality of life and ability to work.
The risk of exposure is even more severe in indoor environments where the generation and collection of fog particles is conducive.
Excessive or prolonged exposure to metalworking fluid mist can lead to a variety of long-term health conditions:
- Nasal and eye irritation
- Occupational exogenous allergic alveolitis (EAA)
- Occupational asthma
Risk control is difficult
Employers have a responsibility to control exposure to hazardous substances, and suppliers have a responsibility to report them, but hazards associated with vaping may not be obvious or immediate.
The question is: what can you do to minimize the health risks to operators exposed to metalworking fluid mist? Less hazardous fluids can be selected in the state of supply. However, there is no such thing as a healthy mist!
Metalworking fluids are often used in open systems that are prone to contamination for a long time. This can be both chemical substances, such as tramp oil, and biological substances, such as bacteria, and endotoxins from living and dead bacterial cells. This begs the question: if you can't 100% control what's in the fluid, how do you control what's in the mist?
How to minimize exposure risk?
One way to minimize the risk of exposure to metalworking fluid mist is to install an effective risk management program. For this, we can adopt the APC method used by HSE for risk assessment:
Avoid
- Replace fluid with less hazardous product.
- Introduce control measures such as equipment and tools.
- Reduce prolonged exposure by installing specific work methods.
Protection
- Ensure proper PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) is available and used.
- Install a suitable Local Exhaust Ventilation (LEV) system to remove fumes and fumes.
- Provide adequate training and education.
Check
- Monitor and record LEV good work.
- Install fluid management system
- Report and record operator health complaints
Fluid Condition Monitoring
It is strongly recommended to implement a fluid condition monitoring program and keep records for at least 5 years.
HDM recommends a balanced fluid condition monitoring program with short-term and long-term analysis:
DAILY/KEY ANALYSIS
- Appearance and smell
- Surface oil layer, emulsion layer and water layer
- Refractometer concentration
weekly-biweekly
- temperature
- record pH
- Bacteria and fungi
Monthly/Less Important
- water hardness
- Conductivity
- Foaming
- filter
When using metalworking fluids, it is critical that concentrations and operating conditions are within the recommended ranges.
choose the right product
Another way to minimize the risk of metalworking fluid fogging is to choose the best product that combines health and safety with performance and economy.
It is also important to consider the products used throughout the processing cycle. For example, a more expensive and dangerous product may actually be a safer long-term option because it protects the fluid and thus the operator from harmful microorganisms.
HDM offers a complete line of pure and soluble metalworking fluids designed to achieve the optimum balance of safety, productivity and economy throughout the life of the fluid in use.









